Explore the quadtree data structure for spatial data partitioning.
Let’s explore another data structure to find nearby restaurants on Yelp or Google Maps.
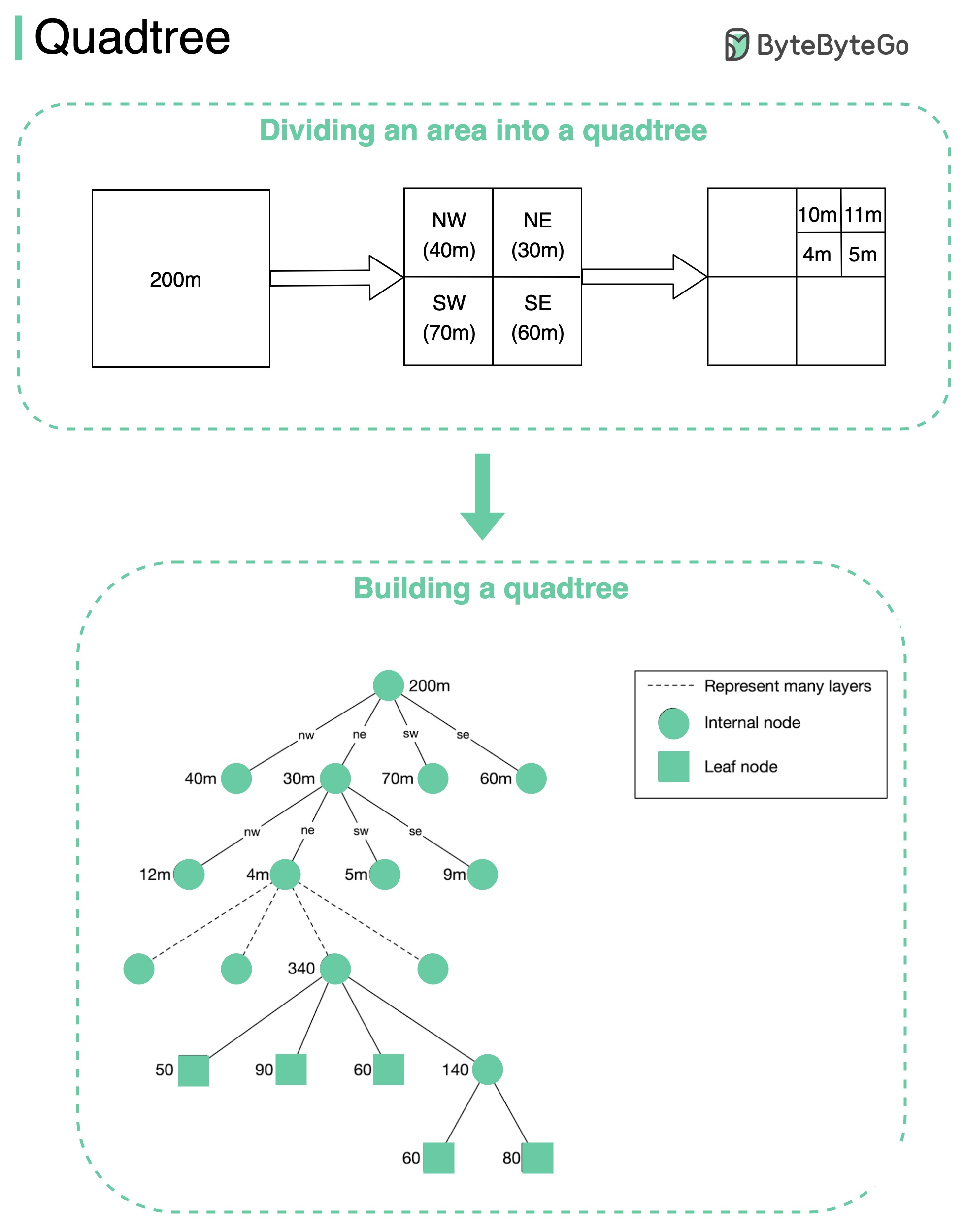
A quadtree is a data structure that is commonly used to partition a two-dimensional space by recursively subdividing it into four quadrants (grids) until the contents of the grids meet certain criteria.
A quadtree is an in-memory data structure and it is not a database solution. It runs on each LBS (Location-Based Service, see last week’s post) server, and the data structure is built at server start-up time.
The second diagram explains the quadtree building process in more detail. The root node represents the whole world map. The root node is recursively broken down into 4 quadrants until no nodes are left with more than 100 businesses.
Build the quadtree in memory.
After the quadtree is built, start searching from the root and traverse the tree, until we find the leaf node where the search origin is.
If that leaf node has 100 businesses, return the node. Otherwise, add businesses from its neighbors until enough businesses are returned.
It may take a few minutes to build a quadtree in memory with 200 million businesses at the server start-up time.
While the quadtree is being built, the server cannot serve traffic.
Therefore, we should roll out a new release of the server incrementally to a small subset of servers at a time. This avoids taking a large swathe of the server cluster offline and causes service brownout.