Explore the inner workings of search engines: crawling, indexing, and ranking.
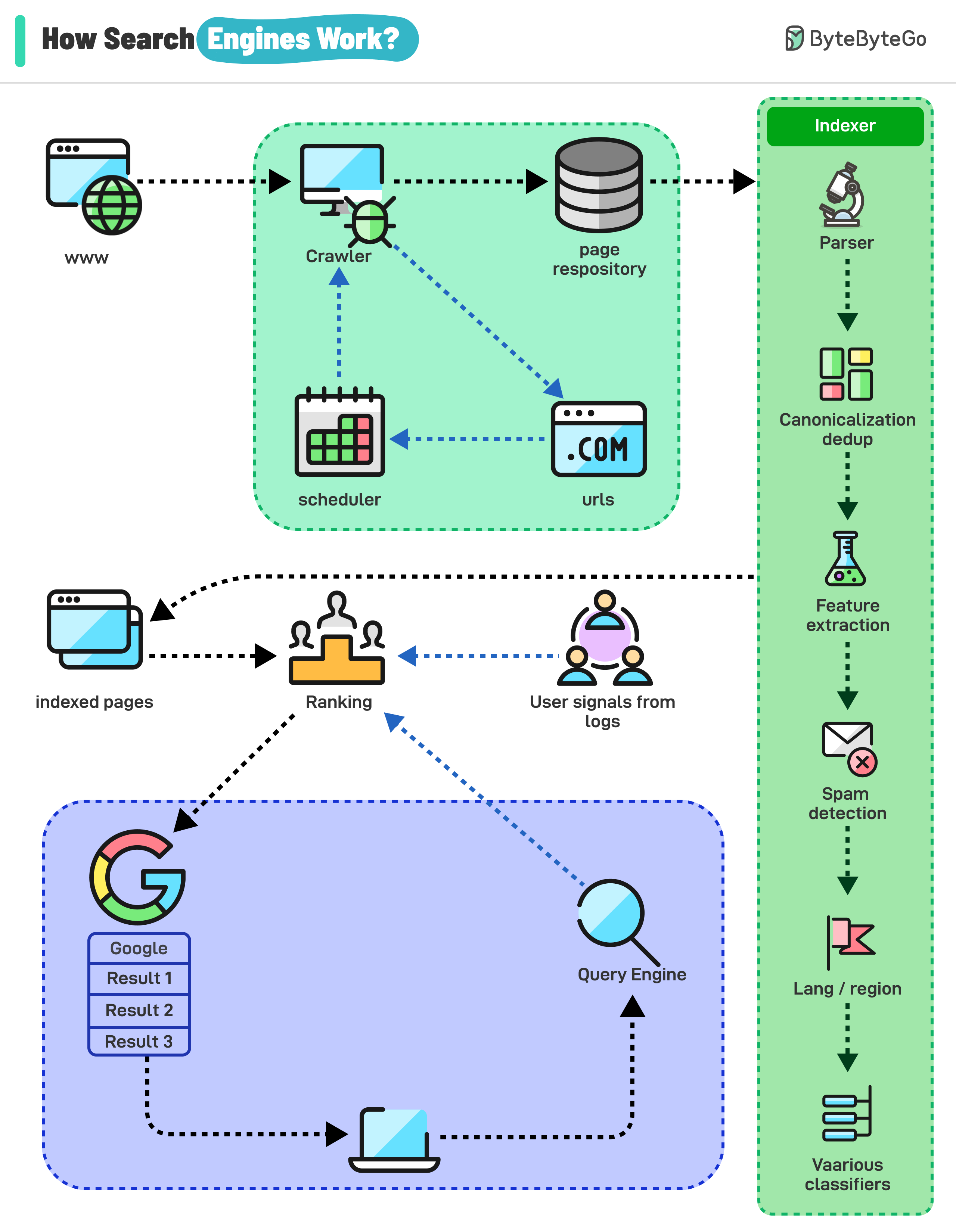
Search engines work through a combination of three core processes:
Search engines use automated programs called “crawlers” to discover and download web pages from the internet. These crawlers start with a list of known web pages (seeds) and follow links on those pages to find new ones, creating a vast network of interconnected content.
The information collected by the crawlers is then analyzed and organized into a massive database called an index. This process involves extracting key elements such as keywords, content type, freshness, language, and other classification signals to understand what each page is about and how relevant it might be to different search queries.
When a user enters a query, the search engine’s algorithm sifts through the index to identify the most relevant and helpful pages. Here’s a breakdown of how it works: