Explore the top use cases for distributed locks in distributed systems.
A distributed lock is a mechanism that ensures mutual exclusion across a distributed system.
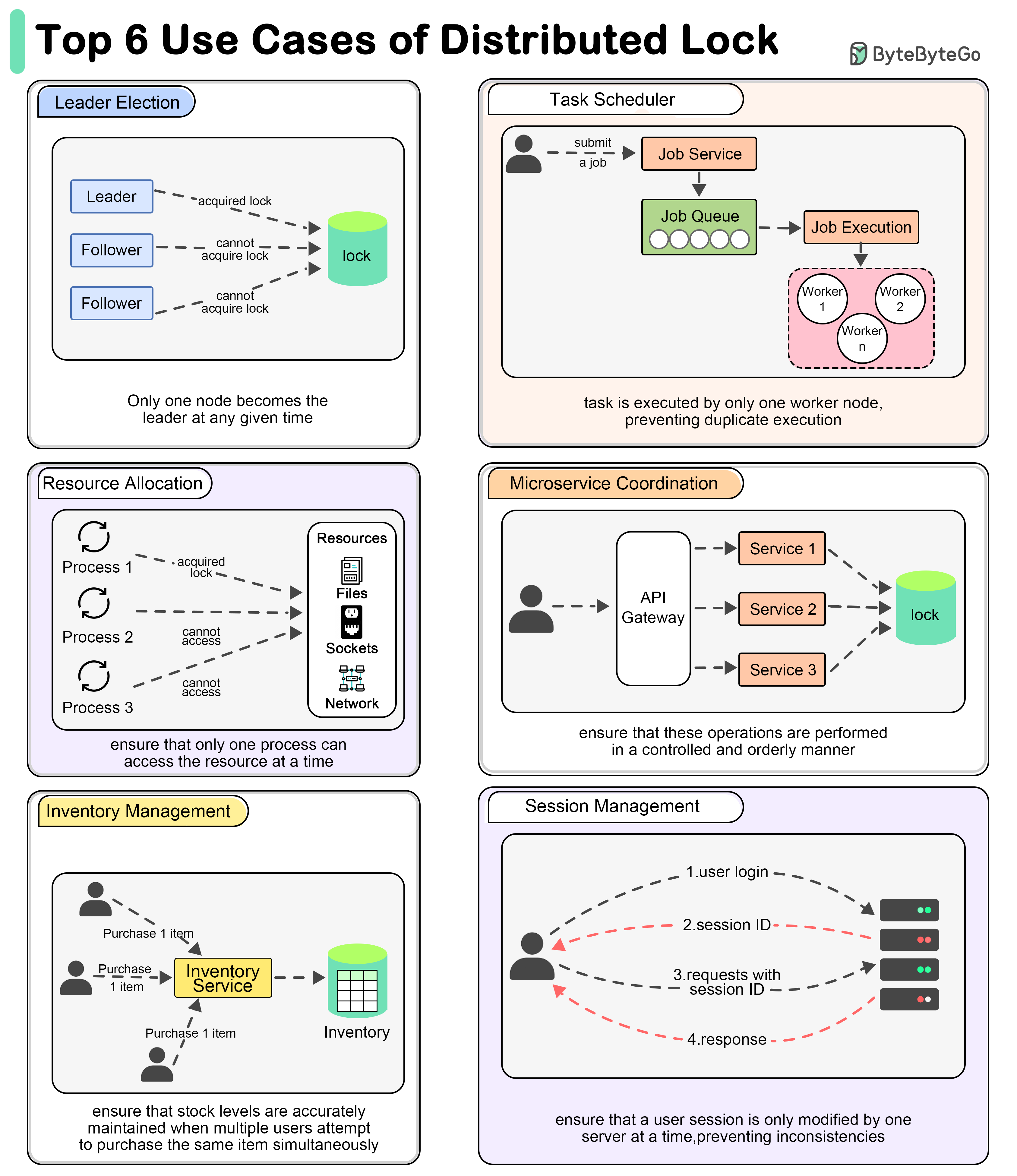
Leader Election
Distributed locks can be used to ensure that only one node becomes the leader at any given time.
Task Scheduling
In a distributed task scheduler, distributed locks ensure that a scheduled task is executed by only one worker node, preventing duplicate execution.
Resource Allocation
When managing shared resources like file systems, network sockets, or hardware devices, distributed locks ensure that only one process can access the resource at a time.
Microservices Coordination
When multiple microservices need to perform coordinated operations, such as updating related data in different databases, distributed locks ensure that these operations are performed in a controlled and orderly manner.
Inventory Management
In e-commerce platforms, distributed locks can manage inventory updates to ensure that stock levels are accurately maintained when multiple users attempt to purchase the same item simultaneously.
Session Management
When handling user sessions in a distributed environment, distributed locks can ensure that a user session is only modified by one server at a time, preventing inconsistencies.