Explore TCP and UDP protocols in online gaming for data transmission.
A common practice is to use RUDP (Reliable UDP). It adds a reliable mechanism on top of UDP to provide much lower latency than TCP and guarantee accuracy.
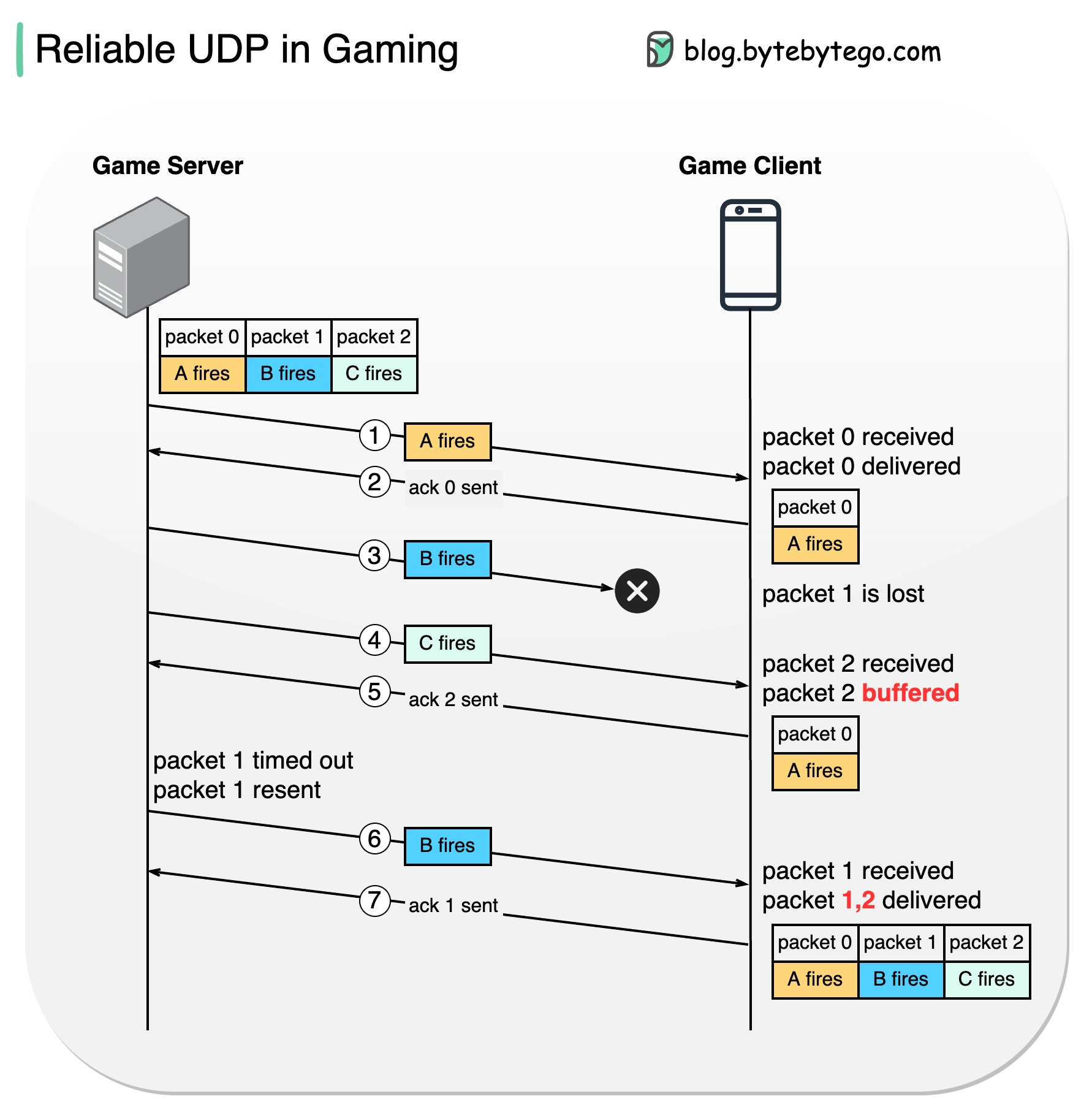
The diagram below shows how reliable data delivery is implemented in online gaming to get eventually-synchronized states.
Suppose there is a big fight in a simulation shooter game. Characters A, B, and C open fires in sequence. How does the game server transmit the states from the game server to the game client?
Steps 1 and 2 - Character A opens fires. The packet (packet 0) is sent to the client. The client acknowledges the server.
Step 3 - Character B opens fire. The packet is lost during transmission.
Steps 4 and 5 - Character C opens fire. The packet (packet 2) is sent to the client. Since the last successfully delivered packet is packet 0, the client knows that packet 1 is lost, so packet 2 is buffered on the client side. The client acknowledges the server for the reception of packet 2.
Steps 6 and 7 - The server doesn’t receive the ack for packet 1 for a while, so it resends packet 1. When the client receives packet 1, all the subsequent packets become effective, so packets 1 and 2 become “delivered”. The client then acknowledges the server for the reception of packet 1. No packets are buffered at this point.