Explore the key factors behind AWS Lambda's impressive speed.
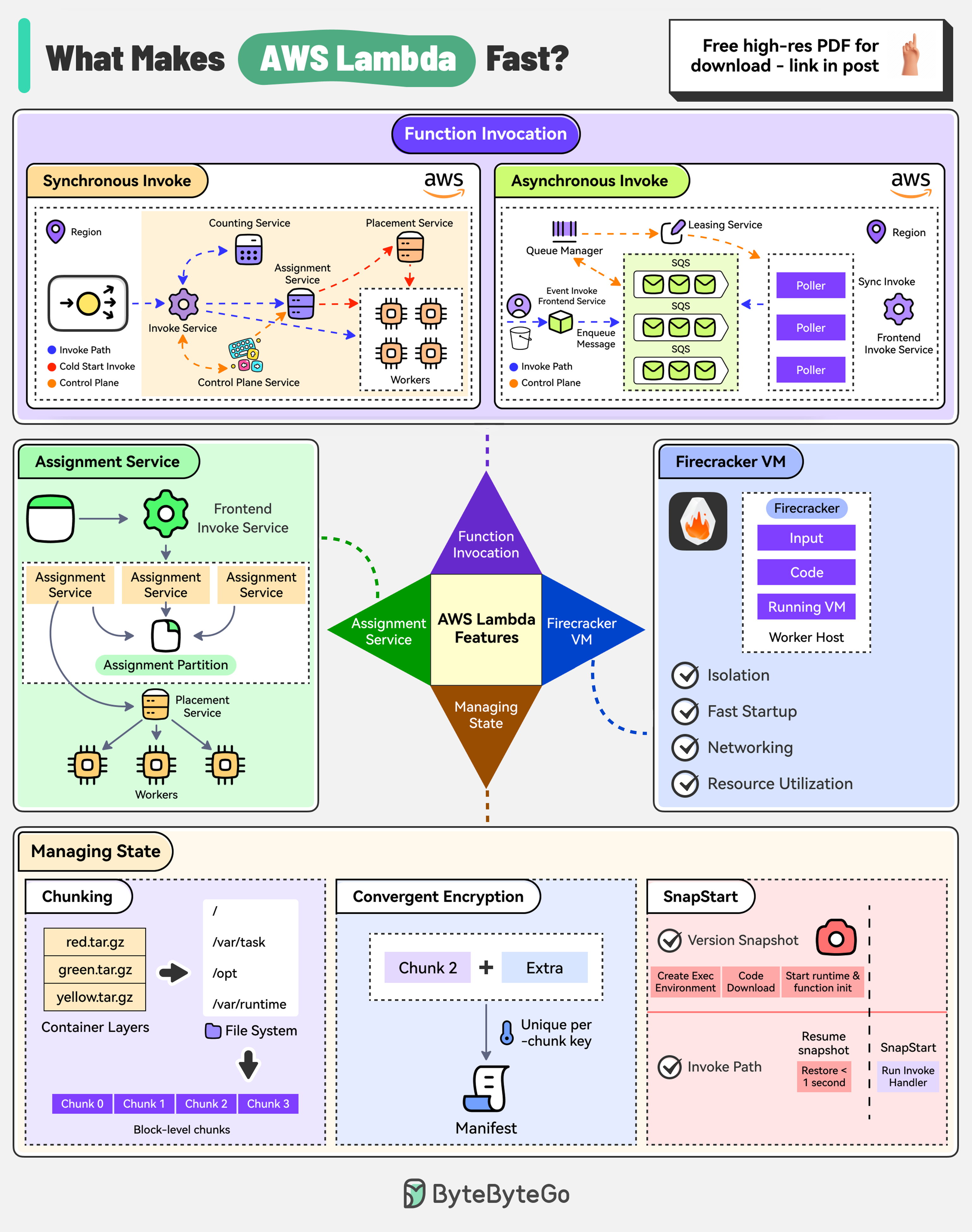
There are 4 main pillars:
AWS Lambda supports synchronous and asynchronous invocation.
In synchronous invocation, the caller directly calls the Lambda function using AWS CLI, SDK, or other services.
In asynchronous invocation, the caller doesn’t wait for the function’s response. The request is authorized and an event is placed in an internal SQS queue. Pollers read messages from the queue and send them for processing.
The Assignment Service manages the execution environments.
The service is written in Rust for high performance and is divided into multiple partitions with a leader-follower approach for high availability.
The state of execution environments is written to an external journal log.
Firecracker is a lightweight virtual machine manager designed for running serverless workloads such as AWS Lambda and AWS Fargate.
It uses Linux’s Kernel-based virtual machine to create and manage secure, fast-booting microVMs.
AWS Lambda also has to manage the state consisting of input data and function code.
To make it efficient, it uses multiple techniques: