Distributes network traffic across multiple servers to optimize resources.
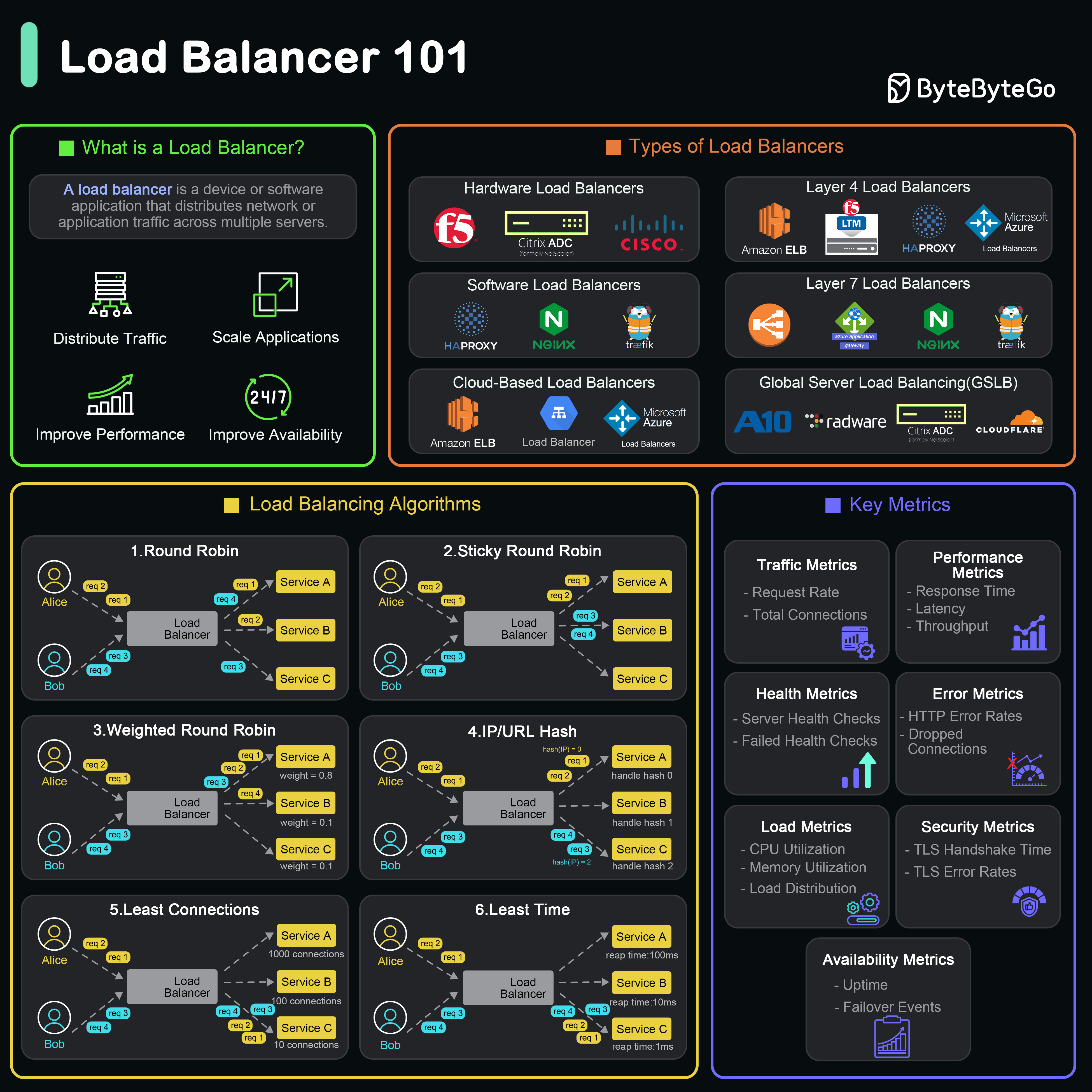
A load balancer is a device or software application that distributes network or application traffic across multiple servers.
What Does a Load Balancer Do?
Types of Load Balancers