Explore eventual consistency patterns for distributed database design.
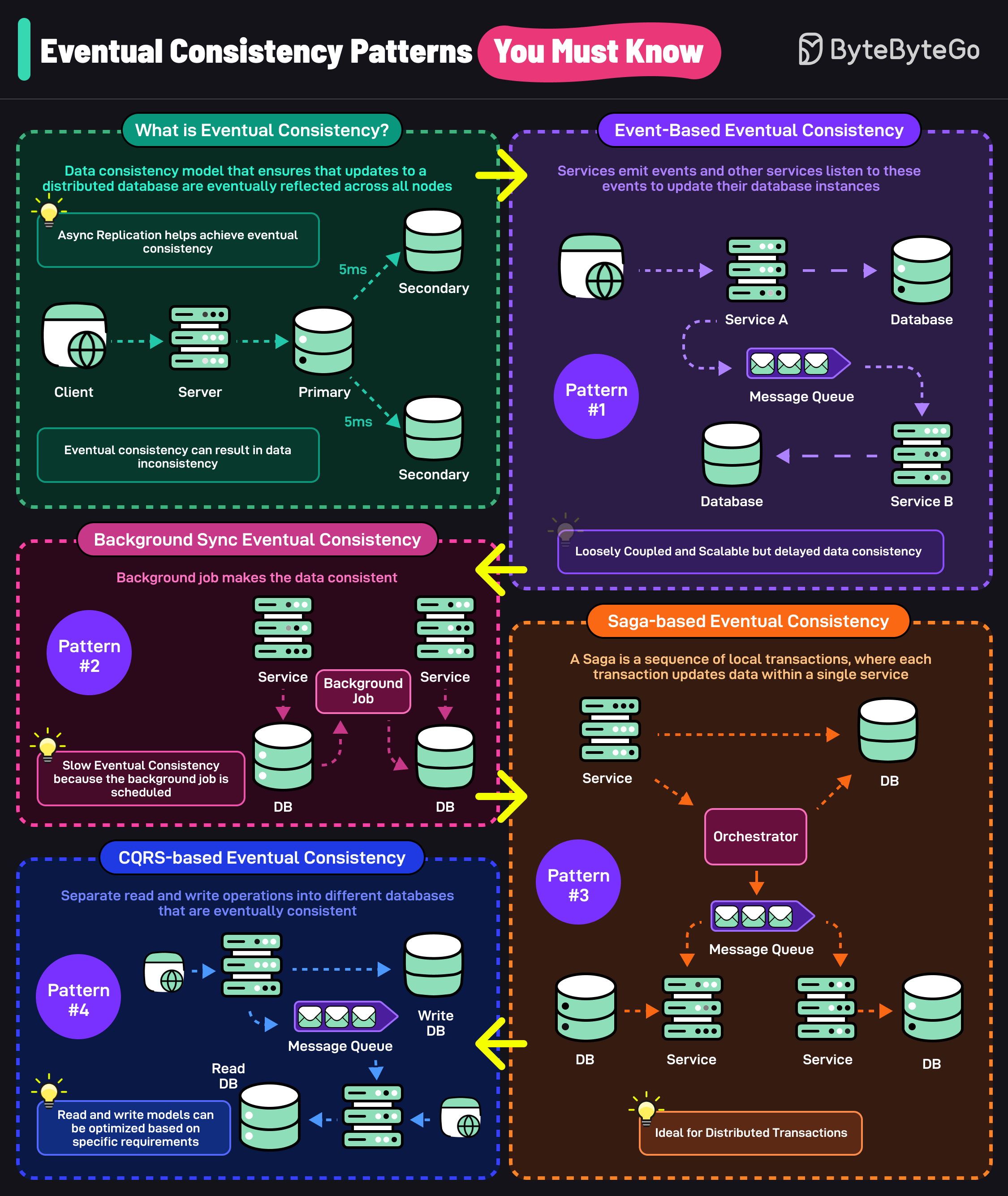
Eventual consistency is a data consistency model that ensures that updates to a distributed database are eventually reflected across all nodes. Techniques like async replication help achieve eventual consistency.
However, eventual consistency can also result in data inconsistency. Here are 4 patterns that can help you design applications.
Services emit events and other services listen to these events to update their database instances. This makes services loosely coupled but delays data consistency.
In this pattern, a background job makes the data across databases consistent. It results in slower eventual consistency since the background job runs on a specific schedule.
Saga is a sequence of local transactions where each transaction updates data with a single service. It is used to manage long-lived transactions that are eventually consistent.
Separate read and write operations into different databases that are eventually consistent. Read and write models can be optimized for specific requirements.