Explore the top 4 use cases for UDP: streaming, DNS, multicast, and IoT.
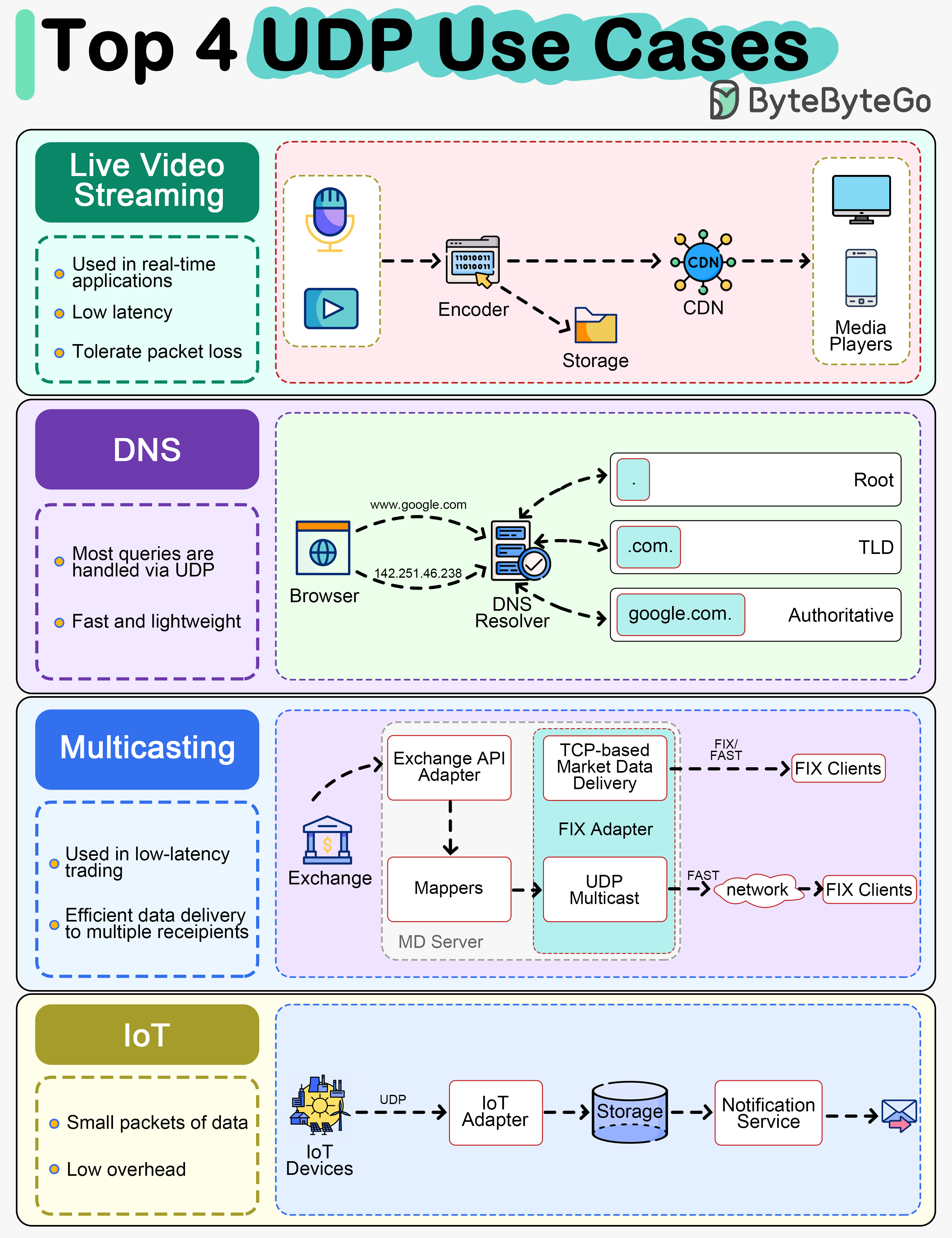
Many VoIP and video conferencing applications leverage UDP due to its lower overhead and ability to tolerate packet loss. Real-time communication benefits from UDP’s reduced latency compared to TCP.
DNS (Domain Name Service) queries typically use UDP for their fast and lightweight nature. Although DNS can also use TCP for large responses or zone transfers, most queries are handled via UDP.
In low-latency trading, UDP is utilized for efficient market data delivery to multiple recipients simultaneously.
UDP is often used in IoT devices for communications, sending small packets of data between devices.