Explore the top data sharding algorithms for efficient data management.
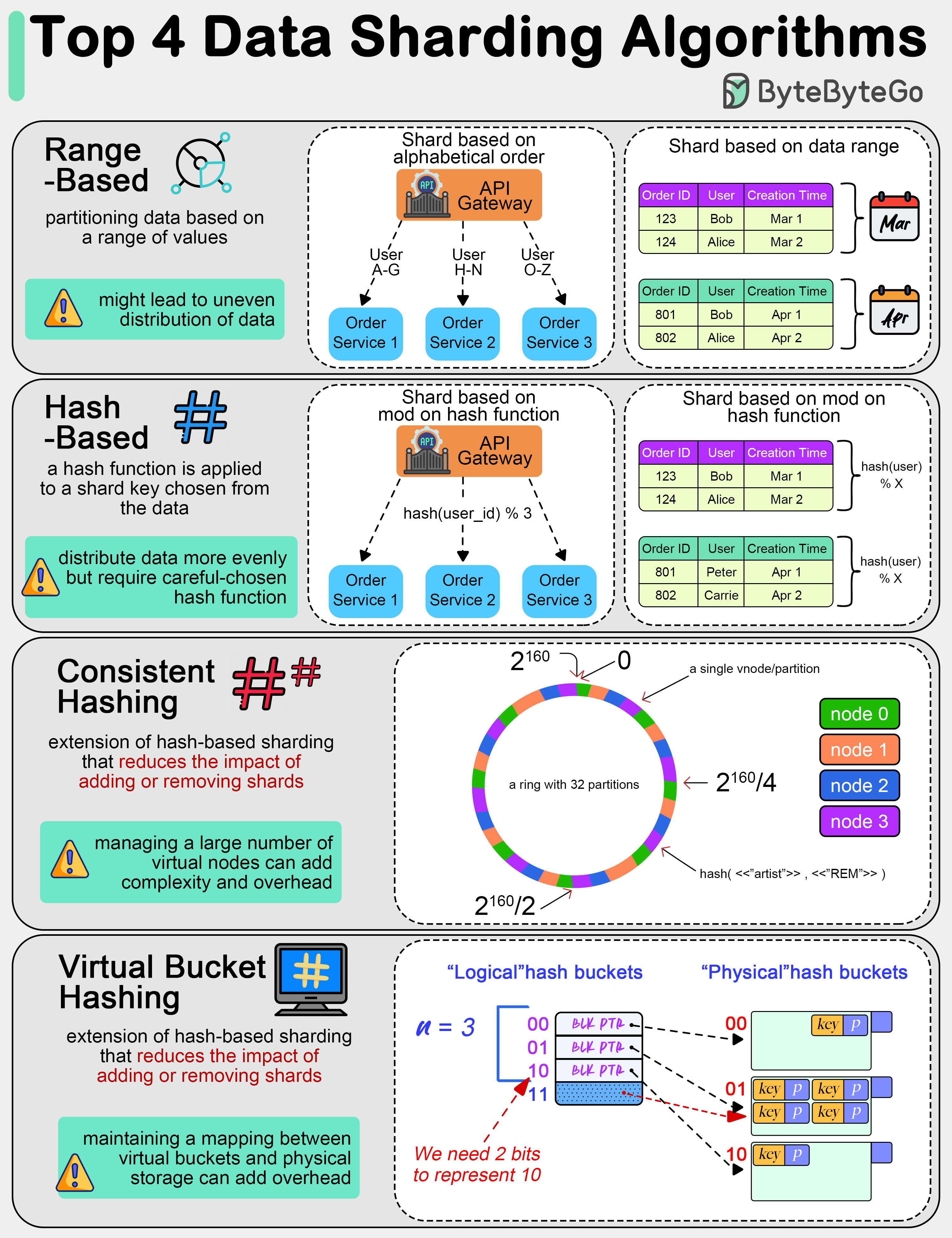
We are dealing with massive amounts of data. Often we need to split data into smaller, more manageable pieces, or “shards”. Here are some of the top data sharding algorithms commonly used:
This involves partitioning data based on a range of values. For example, customer data can be sharded based on alphabetical order of last names, or transaction data can be sharded based on date ranges.
In this method, a hash function is applied to a shard key chosen from the data (like a customer ID or transaction ID).
This tends to distribute data more evenly across shards compared to range-based sharding. However, we need to choose a proper hash function to avoid hash collisions.
This is an extension of hash-based sharding that reduces the impact of adding or removing shards. It distributes data more evenly and minimizes the amount of data that needs to be relocated when shards are added or removed.
Data is mapped into virtual buckets, and these buckets are then mapped to physical shards. This two-level mapping allows for more flexible shard management and rebalancing without significant data movement.