Explore the core principles of object-oriented programming (OOP).
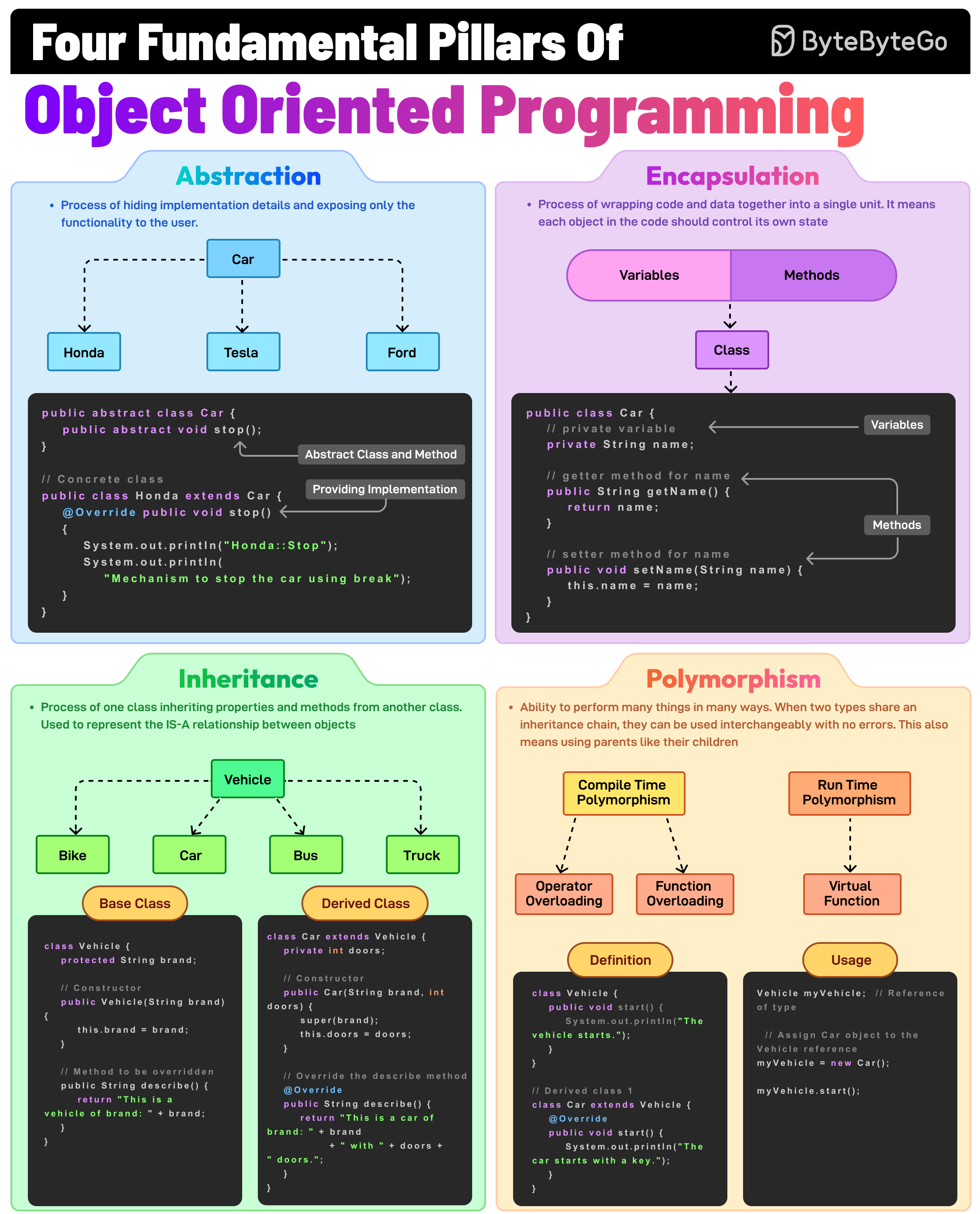
Abstraction, Encapsulation, Inheritance, and Polymorphism are the four pillars of object-oriented programming. What do they mean?
This is the process of hiding implementation details and showing only the essential features of an object. For example, a Vehicle class with an abstract stop method.
It involves wrapping data (fields) and methods in a single unit (class) and restricting direct access using access modifiers. For example, private fields with public getters and setters.
The process of creating a new class (child) that inherits attributes and methods from an existing class (parent), thereby promoting code reuse. For example, a Car class inherits from a Vehicle class.
It allows methods to perform differently based on the object they are invoked on. When two types share an inheritance chain, they can be used interchangeably with no errors.