Explore key use cases for load balancers in modern architectures.
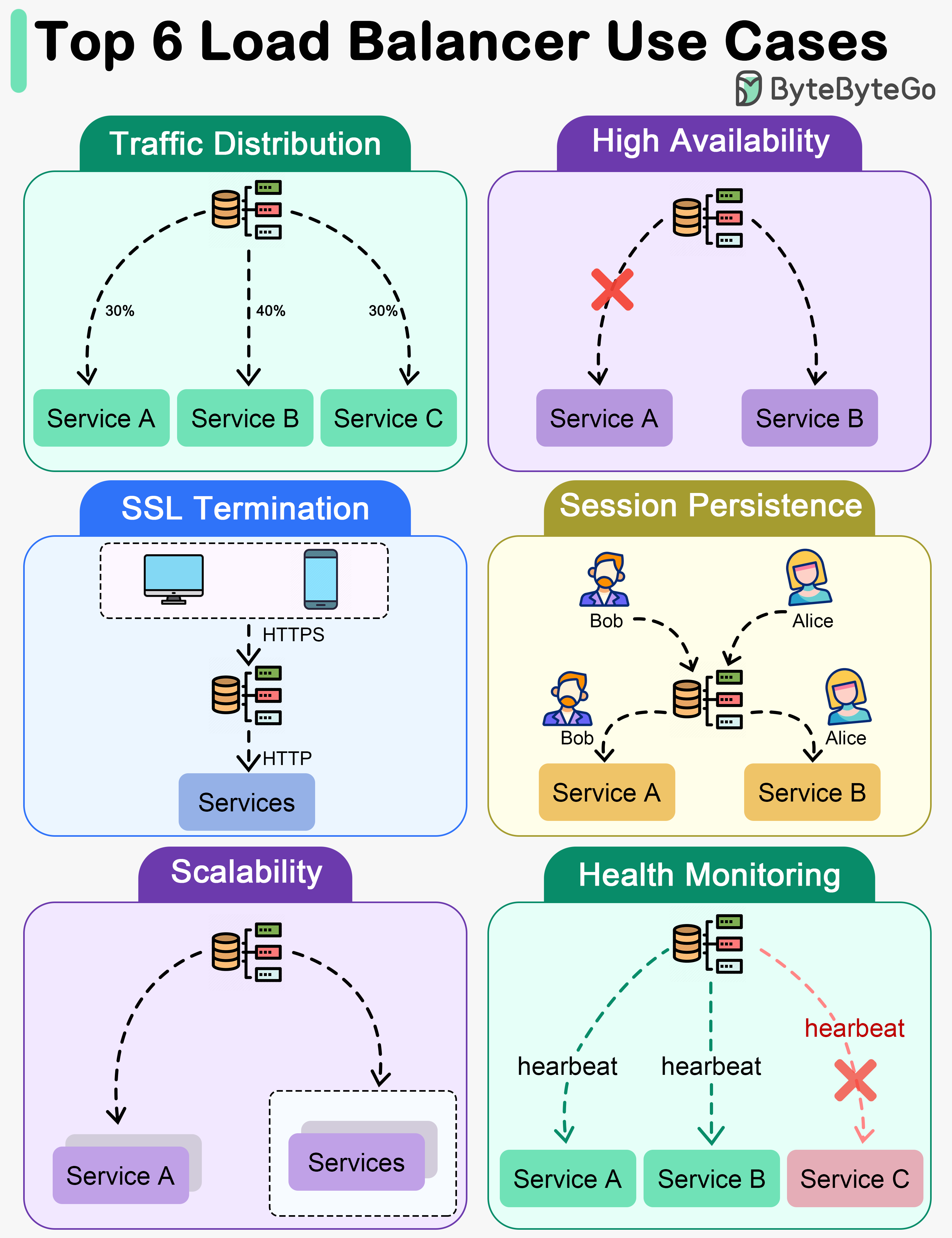
The diagram above shows the top 6 use cases where we use a load balancer.
Traffic Distribution Load balancers evenly distribute incoming traffic among multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed. This helps maintain optimal performance, scalability, and reliability of applications or websites.
High Availability Load balancers enhance system availability by rerouting traffic away from failed or unhealthy servers to healthy ones. This ensures uninterrupted service even if certain servers experience issues.
SSL Termination Load balancers can offload SSL/TLS encryption and decryption tasks from backend servers, reducing their workload and improving overall performance.
Session Persistence For applications that require maintaining a user’s session on a specific server, load balancers can ensure that subsequent requests from a user are sent to the same server.
Scalability Load balancers facilitate horizontal scaling by effectively managing increased traffic. Additional servers can be easily added to the pool, and the load balancer will distribute traffic across all servers.
Health Monitoring Load balancers continuously monitor the health and performance of servers, removing failed or unhealthy servers from the pool to maintain optimal performance.