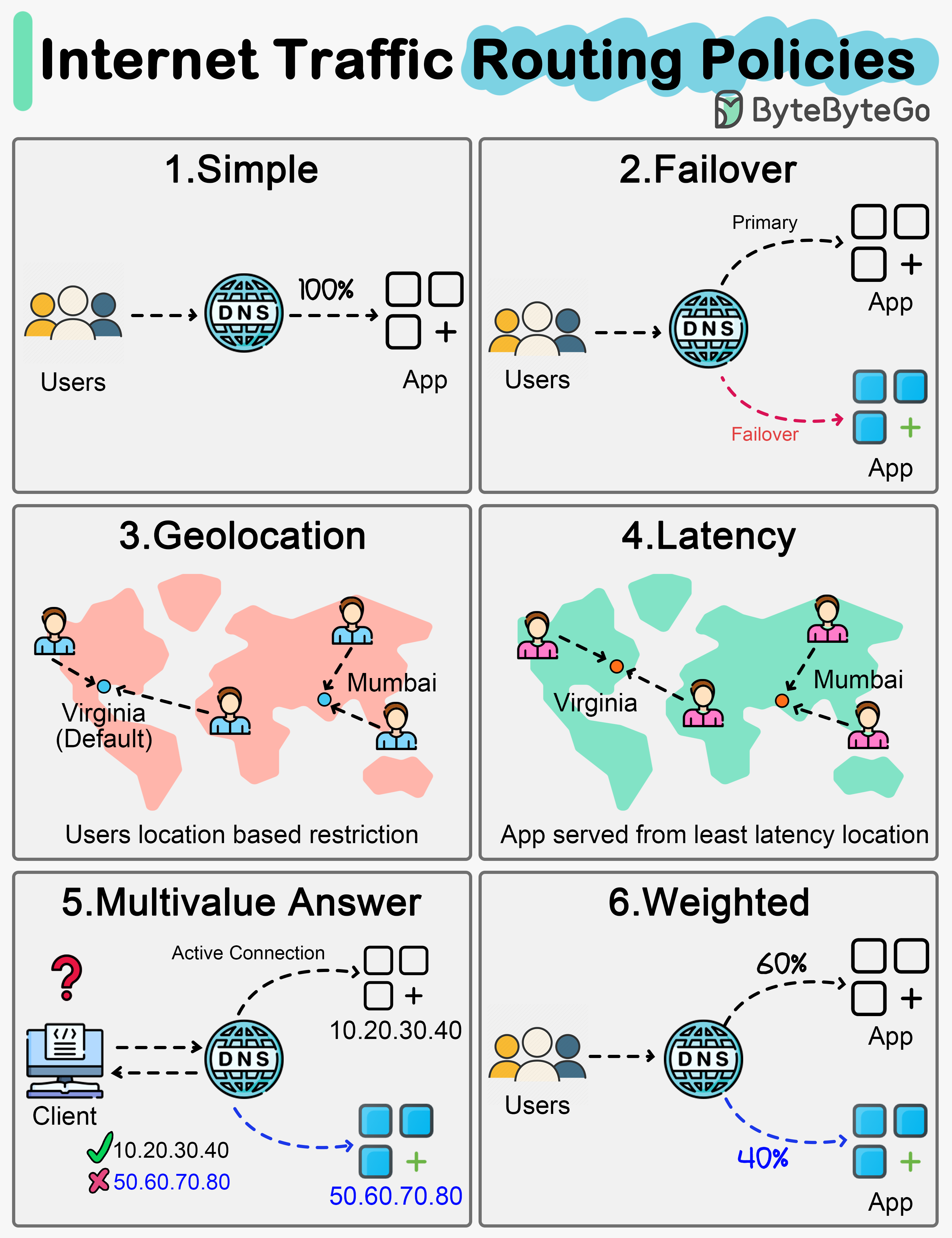
Internet traffic routing policies (DNS policies) play a crucial role in efficiently managing and directing network traffic. Let’s discuss the different types of policies.
- Simple: Directs all traffic to a single endpoint based on a standard DNS query without any special conditions or requirements.
- Failover: Routes traffic to a primary endpoint but automatically switches to a secondary endpoint if the primary is unavailable.
- Geolocation: Distributes traffic based on the geographic location of the requester, aiming to provide localized content or services.
- Latency: Directs traffic to the endpoint that provides the lowest latency for the requester, enhancing user experience with faster response times.
- Multivalue Answer: Responds to DNS queries with multiple IP addresses, allowing the client to select an endpoint. However, it should not be considered a replacement for a load balancer.
- Weighted Routing Policy: Distributes traffic across multiple endpoints with assigned weights, allowing for proportional traffic distribution based on these weights.
