Explore imperative, functional, and object-oriented programming paradigms.
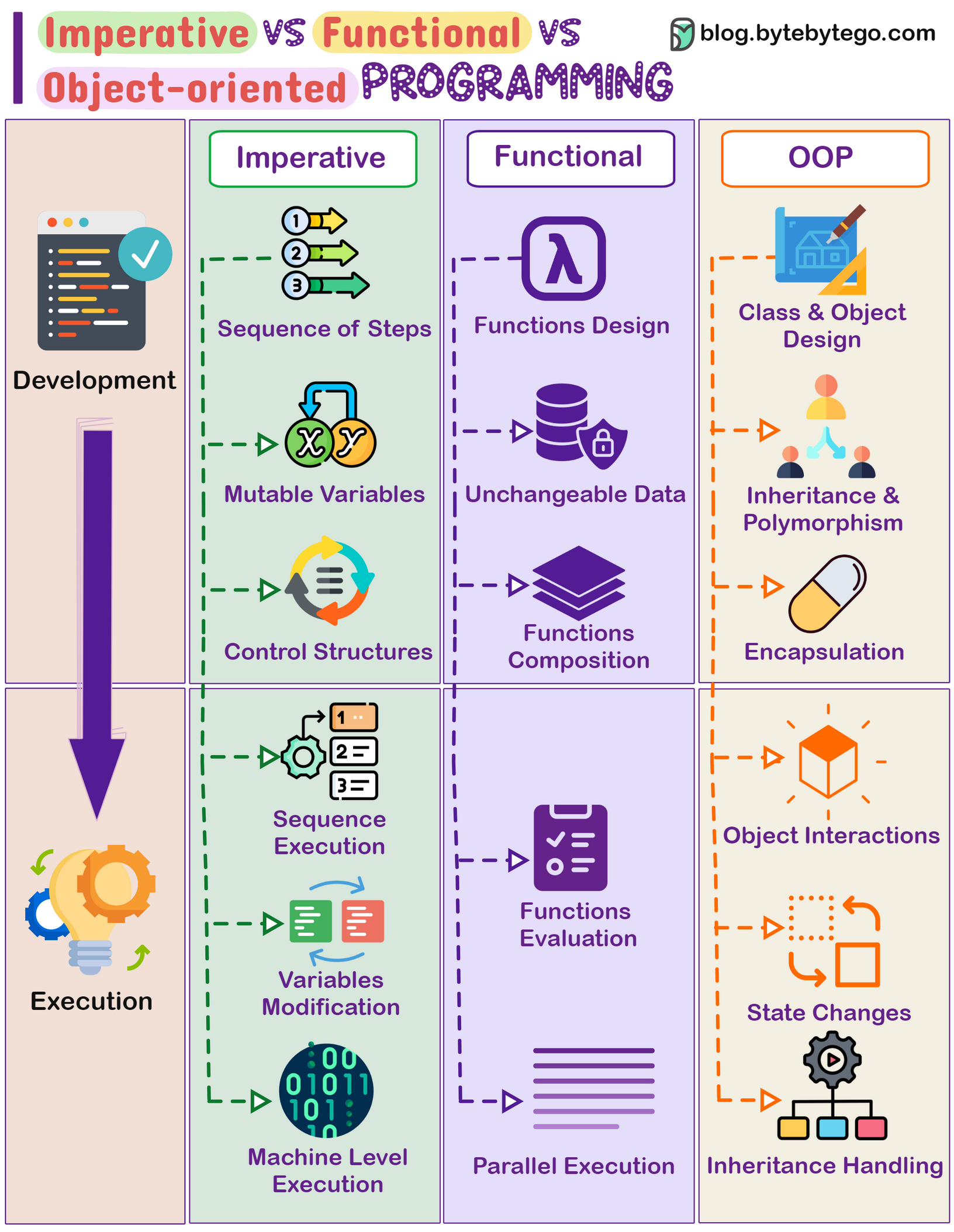
In software development, different programming paradigms offer unique ways to structure code. Three main paradigms are Imperative, Functional, and Object-oriented programming, each with distinct approaches to problem-solving.
Works by changing program state through a sequence of commands.
Uses control structures like loops and conditional statements for execution flow.
Emphasizes mutable data and explicit steps for task completion.
Examples: C, Python, and most procedural languages.
Relies on pure functions, emphasizing computation without side effects.
Promotes immutability and the avoidance of mutable state.
Supports higher-order functions, recursion, and declarative programming.
Examples: Haskell, Lisp, Scala, and functional features in languages like JavaScript.
Focuses on modeling real-world entities as objects, containing data and methods.
Encourages concepts such as inheritance, encapsulation, and polymorphism.
Utilizes classes, objects, and interfaces to structure code.
Examples: Java, C++, Python, and Ruby.