Explore the steps of SQL statement execution within a database system.
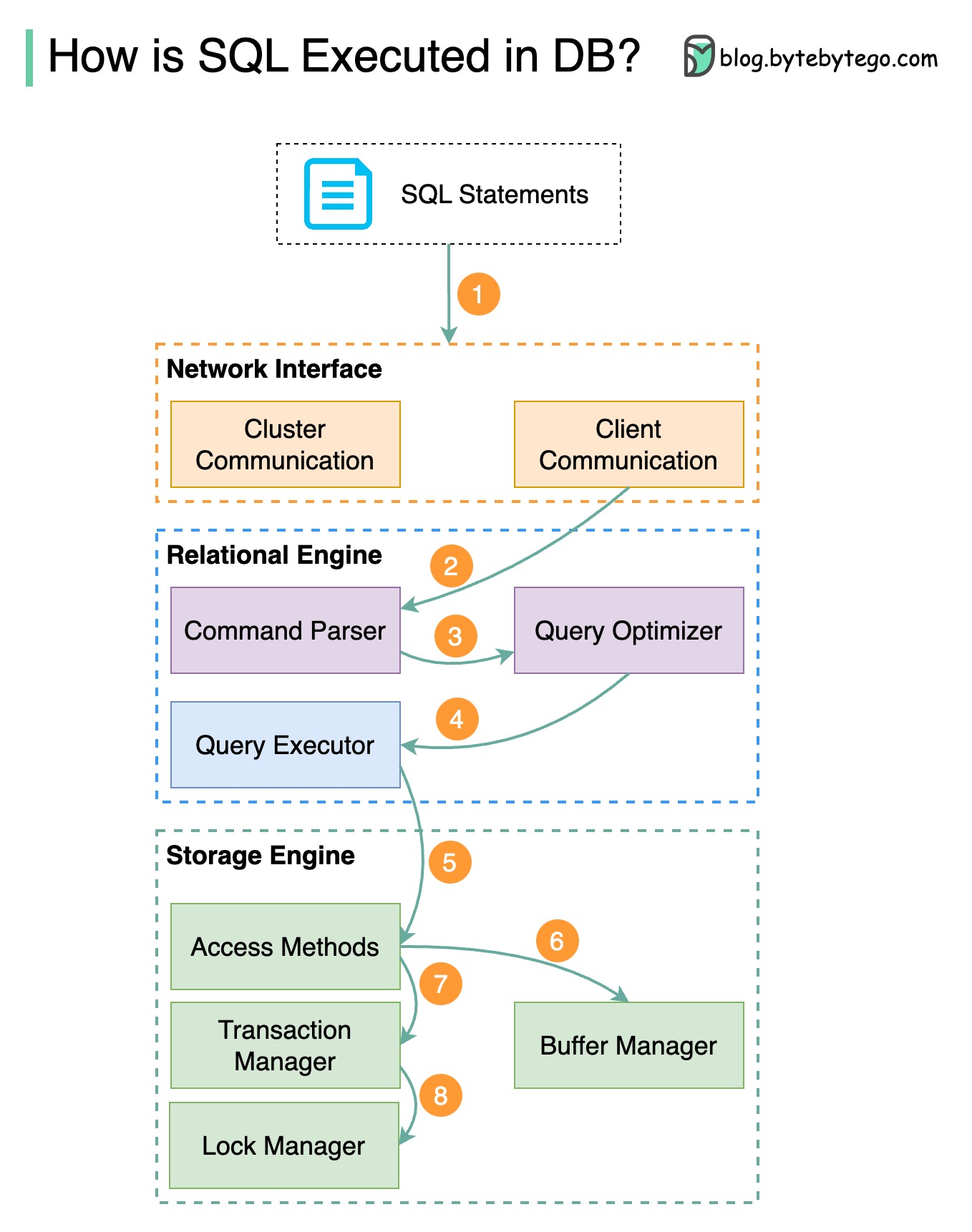
The diagram above shows the process. Note that the architectures for different databases are different, the diagram demonstrates some common designs.
A SQL statement is sent to the database via a transport layer protocol (e.g. TCP).
The SQL statement is sent to the command parser, where it goes through syntactic and semantic analysis, and a query tree is generated afterward.
The query tree is sent to the optimizer. The optimizer creates an execution plan.
The execution plan is sent to the executor. The executor retrieves data from the execution.
Access methods provide the data fetching logic required for execution, retrieving data from the storage engine.
Access methods decide whether the SQL statement is read-only. If the query is read-only (SELECT statement), it is passed to the buffer manager for further processing. The buffer manager looks for the data in the cache or data files.
If the statement is an UPDATE or INSERT, it is passed to the transaction manager for further processing.
During a transaction, the data is in lock mode. This is guaranteed by the lock manager. It also ensures the transaction’s ACID properties.