Explore the inner workings of SSH, a secure network protocol.
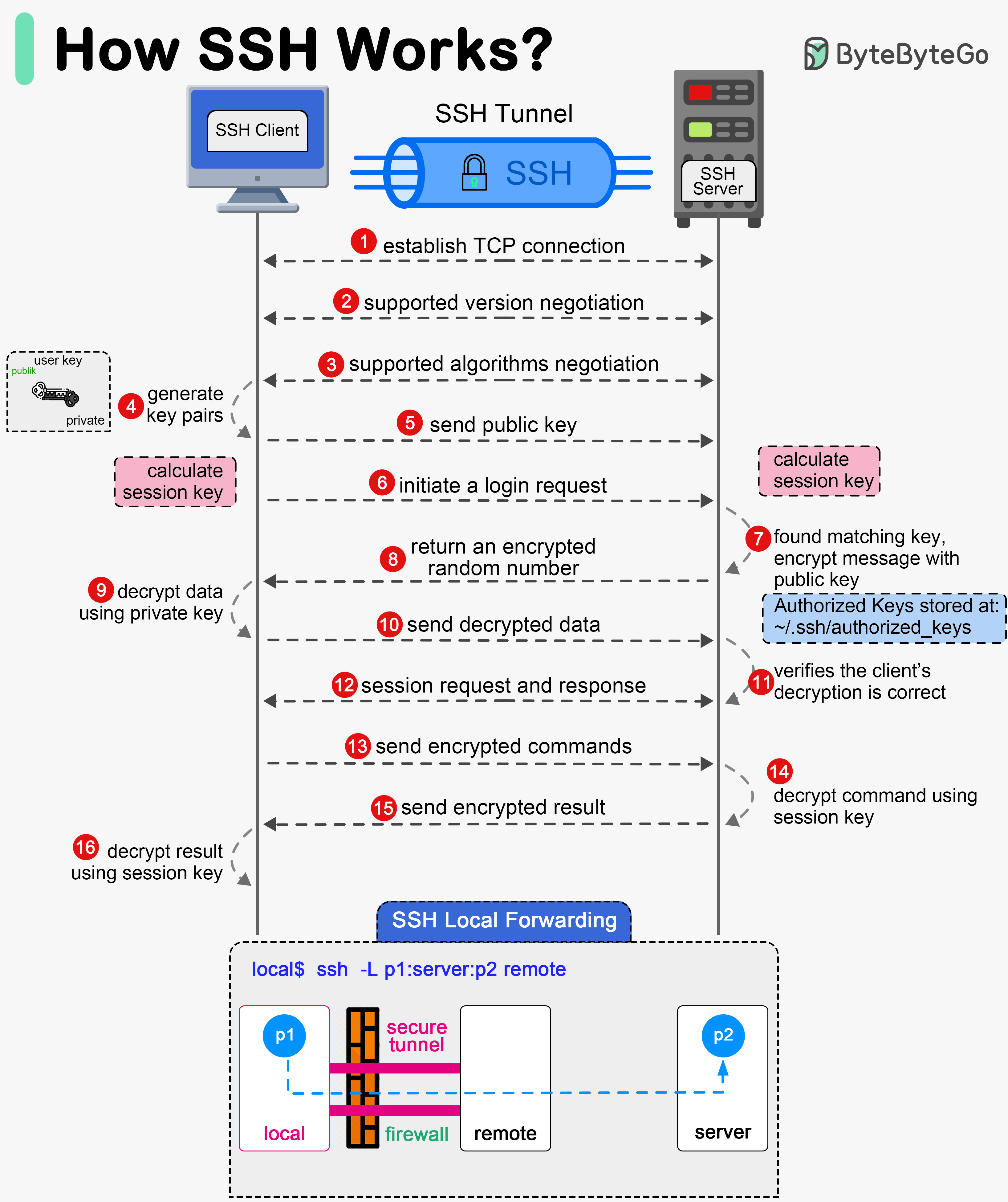
SSH (Secure Shell) is a network protocol used to securely connect to remote machines over an unsecured network. It encrypts the connection and provides various mechanisms for authentication and data transfer.
SSH has two versions: SSH-1 and SSH-2. SSH-2 was standardized by the IETF.
It has three main layers: Transport Layer, Authentication Layer, and Connection Layer.
The Transport Layer provides encryption, integrity, and data protection to ensure secure communication between the client and server.
The Authentication Layer verifies the identity of the client to ensure that only authorized users can access the server.
The Connection Layer multiplexes the encrypted and authenticated communication into multiple logical channels.