Explore the inner workings of AWS Lambda and its serverless architecture.
Serverless is one of the hottest topics in cloud services. How does AWS Lambda work behind the scenes?
Lambda is a serverless computing service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS), which runs functions in response to events.
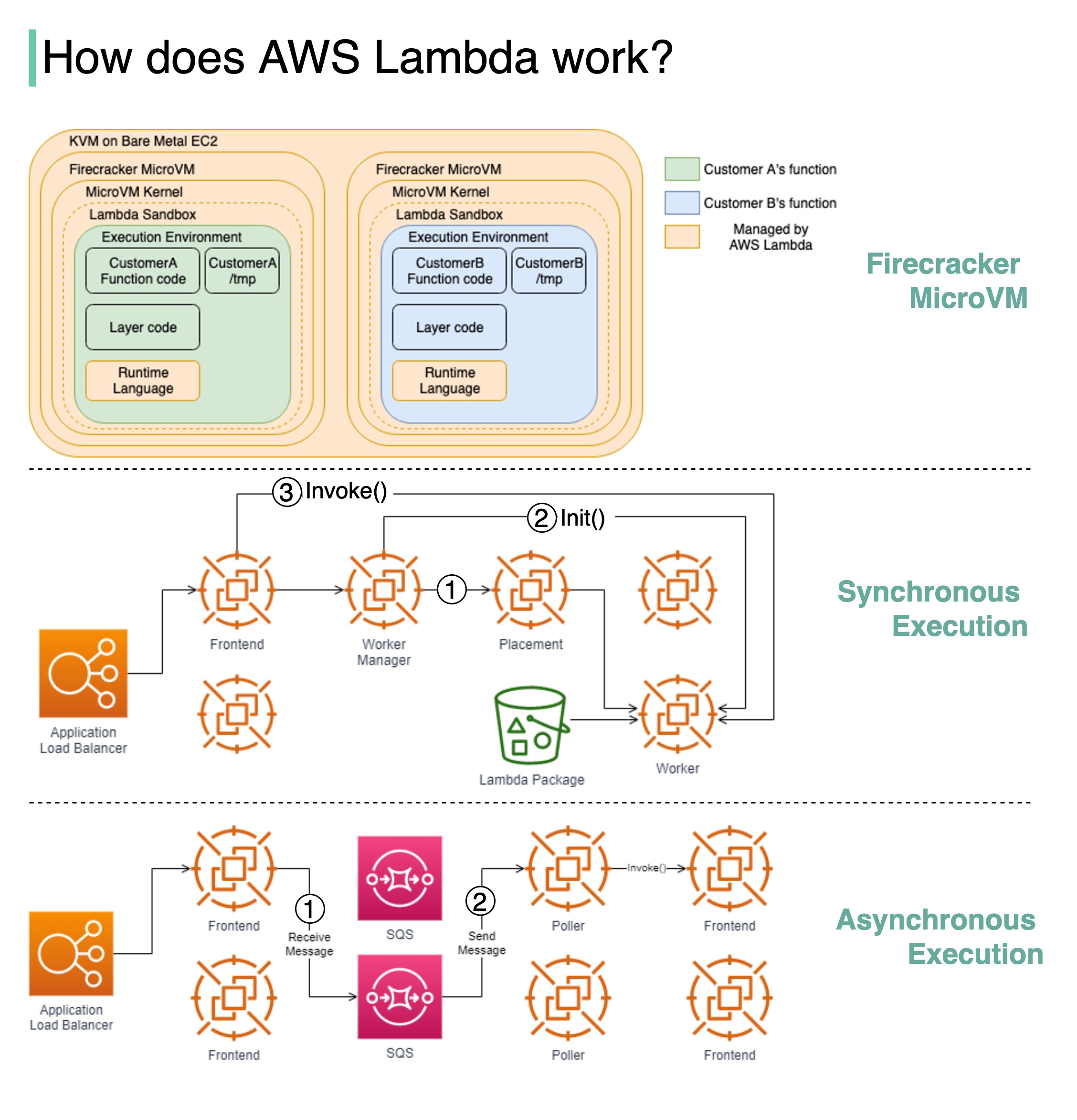
Firecracker is the engine powering all of the Lambda functions. It is a virtualization technology developed at Amazon and written in Rust.
The diagram below illustrates the isolation model for AWS Lambda Workers.
Lambda functions run within a sandbox, which provides a minimal Linux userland, some common libraries and utilities. It creates the Execution environment (worker) on EC2 instances.
How are lambdas initiated and invoked? There are two ways.
Step1: “The Worker Manager communicates with a Placement Service which is responsible to place a workload on a location for the given host (it’s provisioning the sandbox) and returns that to the Worker Manager”.
Step 2: “The Worker Manager can then call Init to initialize the function for execution by downloading the Lambda package from S3 and setting up the Lambda runtime”
Step 3: The Frontend Worker is now able to call Invoke.
Step 1: The Application Load Balancer forwards the invocation to an available Frontend which places the event onto an internal queue(SQS).
Step 2: There is “a set of pollers assigned to this internal queue which are responsible for polling it and moving the event onto a Frontend synchronously. After it’s been placed onto the Frontend it follows the synchronous invocation call pattern which we covered earlier”.