Explore how VPNs create secure connections for online privacy.
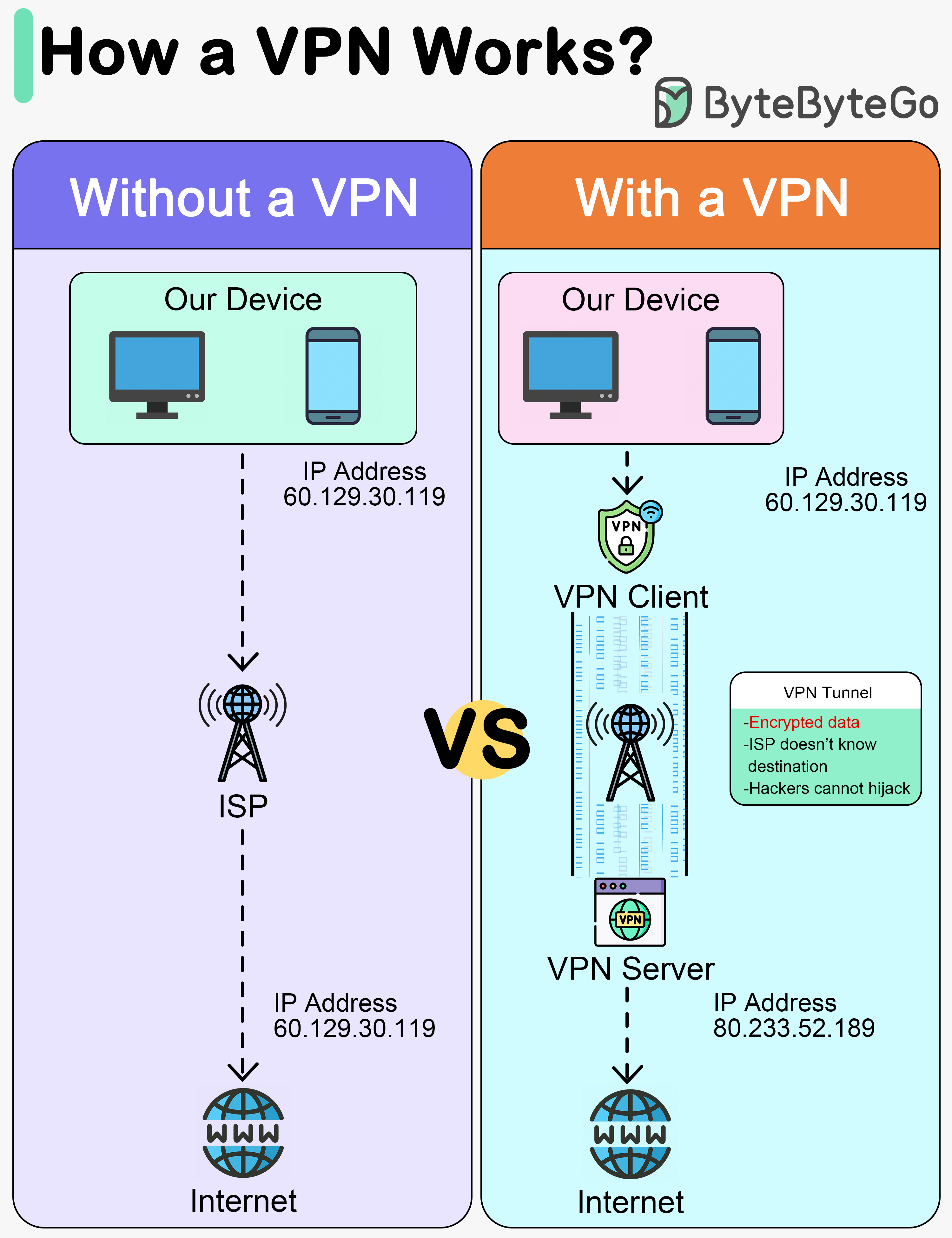
This diagram below shows how we access the internet with and without VPNs.
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a technology that creates a secure, encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the public internet. The primary purpose of a VPN is to provide privacy and security to data and communications.
A VPN acts as a tunnel through which the encrypted data goes from one location to another. Any external party cannot see the data transferring.
A VPN works in 4 steps:
Step 1 - Establish a secure tunnel between our device and the VPN server.
Step 2 - Encrypt the data transmitted.
Step 3 - Mask our IP address, so it appears as if our internet activity is coming from the VPN server.
Step 4 - Our internet traffic is routed through the VPN server.