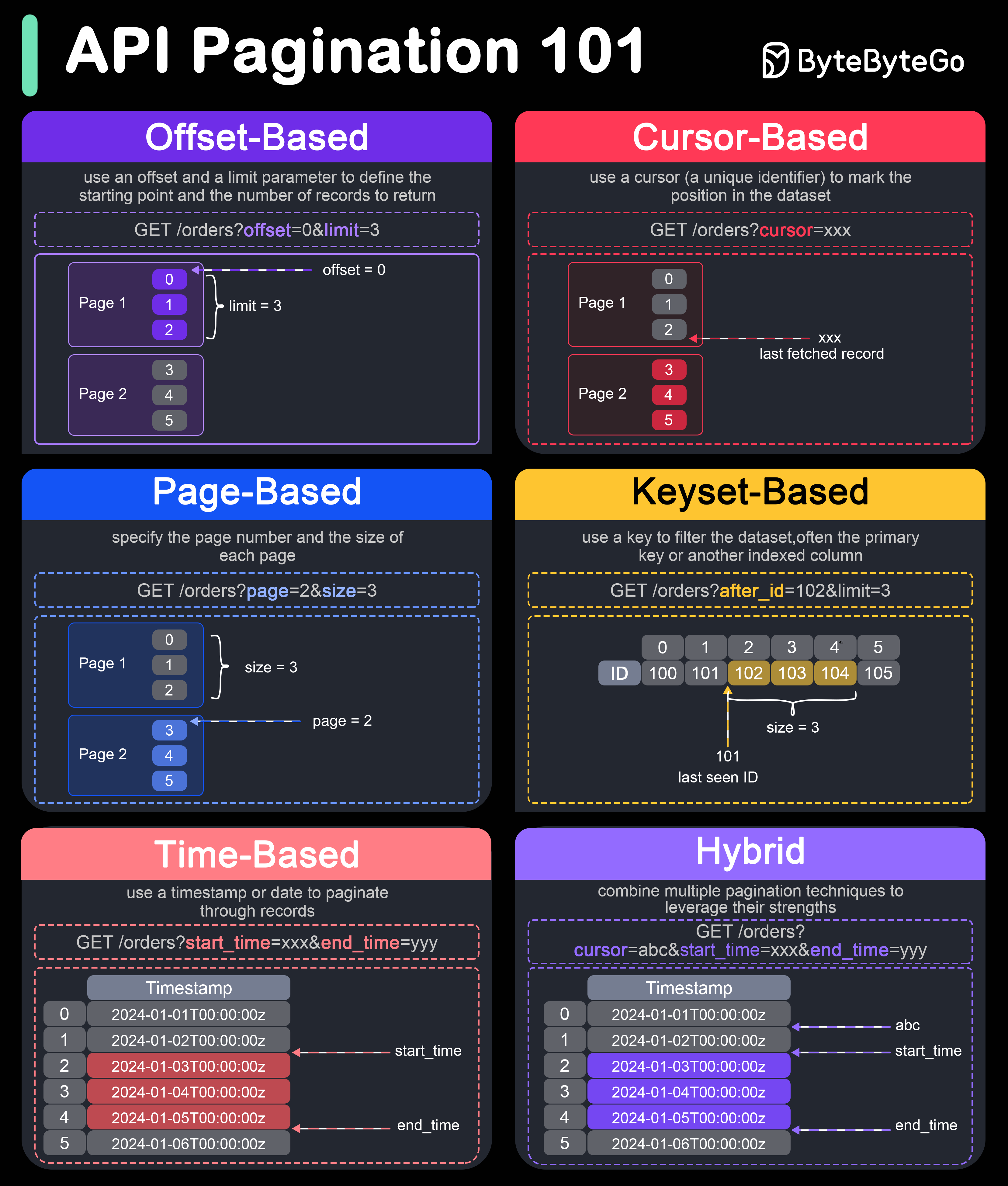
Pagination is crucial in API design to handle large datasets efficiently and improve performance. Here are six popular pagination techniques:
-
Offset-based Pagination:
This technique uses an offset and a limit parameter to define the starting point and the number of records to return.
- Example: GET /orders?offset=0&limit=3
- Pros: Simple to implement and understand.
- Cons: Can become inefficient for large offsets, as it requires scanning and skipping rows.
-
Cursor-based Pagination:
This technique uses a cursor (a unique identifier) to mark the position in the dataset. Typically, the cursor is an encoded string that points to a specific record.
- Example: GET /orders?cursor=xxx
- Pros: More efficient for large datasets, as it doesn’t require scanning skipped records.
- Cons: Slightly more complex to implement and understand.
-
Page-based Pagination:
This technique specifies the page number and the size of each page.
- Example: GET /items?page=2&size=3
- Pros: Easy to implement and use.
- Cons: Similar performance issues as offset-based pagination for large page numbers.
-
Keyset-based Pagination:
This technique uses a key to filter the dataset, often the primary key or another indexed column.
- Example: GET /items?after_id=102&limit=3
- Pros: Efficient for large datasets and avoids performance issues with large offsets.
- Cons: Requires a unique and indexed key, and can be complex to implement.
-
Time-based Pagination:
This technique uses a timestamp or date to paginate through records.
- Example: GET /items?start_time=xxx&end_time=yyy
- Pros: Useful for datasets ordered by time, ensures no records are missed if new ones are added.
- Cons: Requires a reliable and consistent timestamp.
-
Hybrid Pagination:
This technique combines multiple pagination techniques to leverage their strengths.
- Example: Combining cursor and time-based pagination for efficient scrolling through time-ordered records.
- Example: GET /items?cursor=abc&start_time=xxx&end_time=yyy
- Pros: Can offer the best performance and flexibility for complex datasets.
- Cons: More complex to implement and requires careful design.
