Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is a term familiar to most people, as it is used to locate resources on the internet. When you type a URL into a web browser’s address bar, you are accessing a “resource”, not just a webpage.
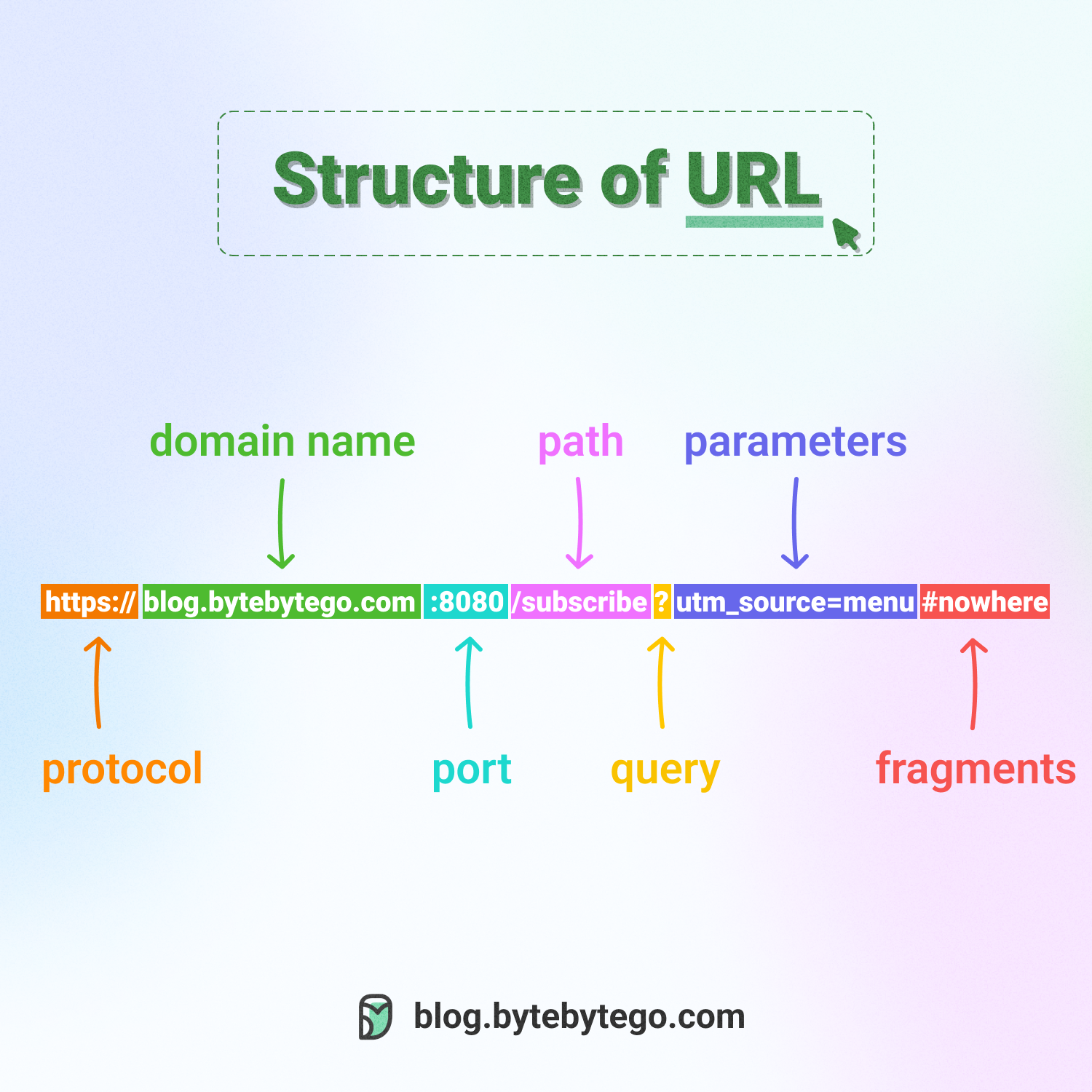
URLs comprise several components:
- The protocol or scheme, such as http, https, and ftp.
- The domain name and port, separated by a period (.)
- The path to the resource, separated by a slash (/)
- The parameters, which start with a question mark (?) and consist of key-value pairs, such as a=b&c=d.
- The fragment or anchor, indicated by a pound sign (#), which is used to bookmark a specific section of the resource.
