Avoid common pitfalls in cloud-native development for robust applications.
By being aware of these anti-patterns and following cloud-native best practices, you can design, build, and operate more robust, scalable, and cost-efficient cloud-native applications.
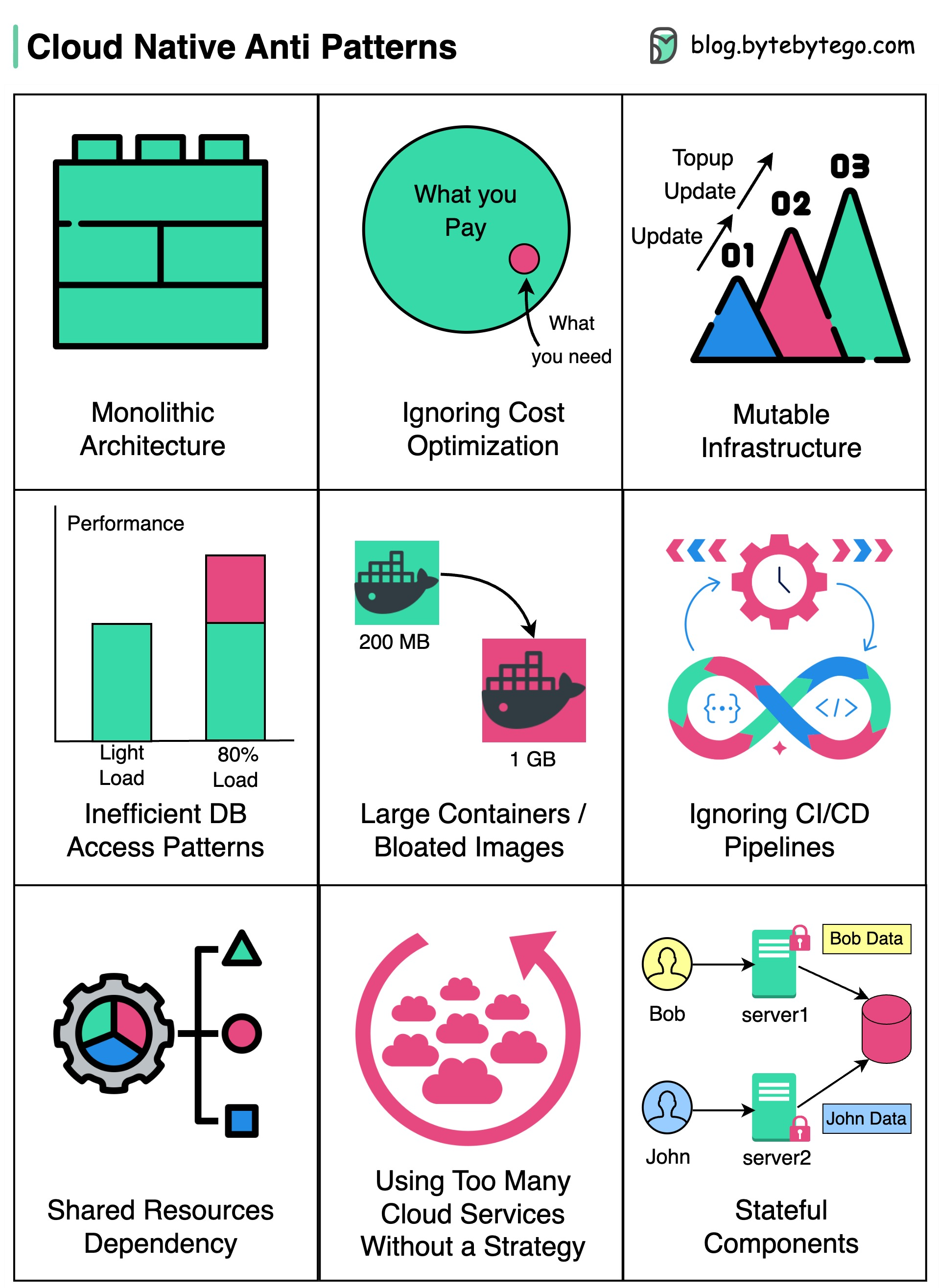
One large, tightly coupled application running on the cloud, hindering scalability and agility.
Cloud services can be expensive, and not optimizing costs can result in budget overruns.
Infrastructure components are to be treated as disposable and are never modified in place.
Failing to embrace this approach can lead to configuration drift, increased maintenance, and decreased reliability.
Use of overly complex queries or lacking database indexing, can lead to performance degradation and database bottlenecks.
Creating large containers or using bloated images can increase deployment times, consume more resources, and slow down application scaling.
Deployments become manual and error-prone, impeding the speed and frequency of software releases.
Applications relying on shared resources like databases can create contention and bottlenecks, affecting overall performance.
While cloud providers offer a vast array of services, using too many of them without a clear strategy can create complexity and make it harder to manage the application.
Relying on persistent state in applications can introduce complexity, hinder scalability, and limit fault tolerance.