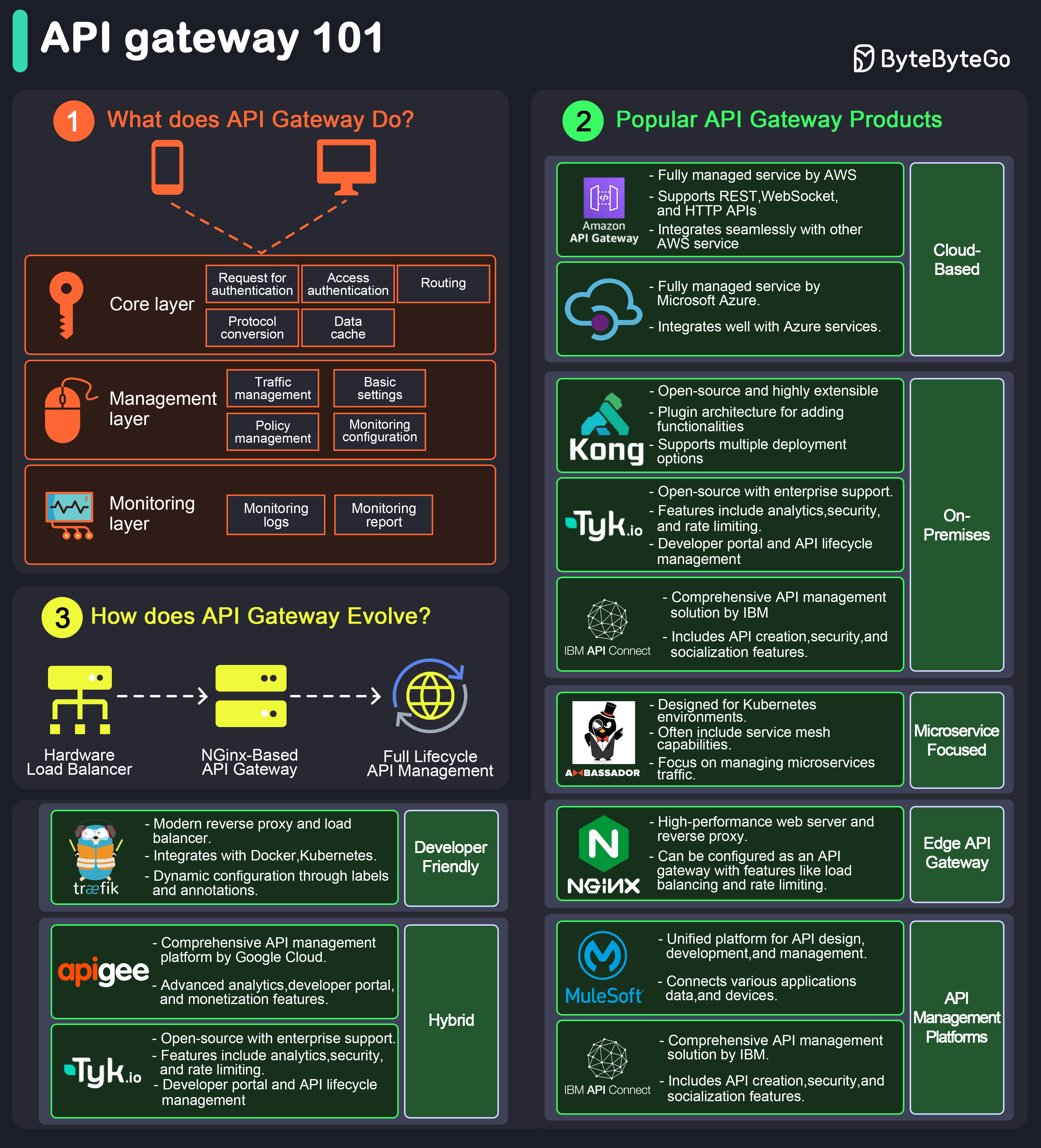
An API gateway is a server that acts as an API front-end, receiving API requests, enforcing throttling and security policies, passing requests to the back-end service, and then returning the appropriate result to the client.
It is essentially a middleman between the client and the server, managing and optimizing API traffic.
Key Functions of an API Gateway
- Request Routing: Directs incoming API requests to the appropriate backend service.
- Load Balancing: Distributes requests across multiple servers to ensure no single server is overwhelmed.
- Security: Implements security measures like authentication, authorization, and data encryption.
- Rate Limiting and Throttling: Controls the number of requests a client can make within a certain period.
- API Composition: Combines multiple backend API requests into a single frontend request to optimize performance.
- Caching: Stores responses temporarily to reduce the need for repeated processing.
