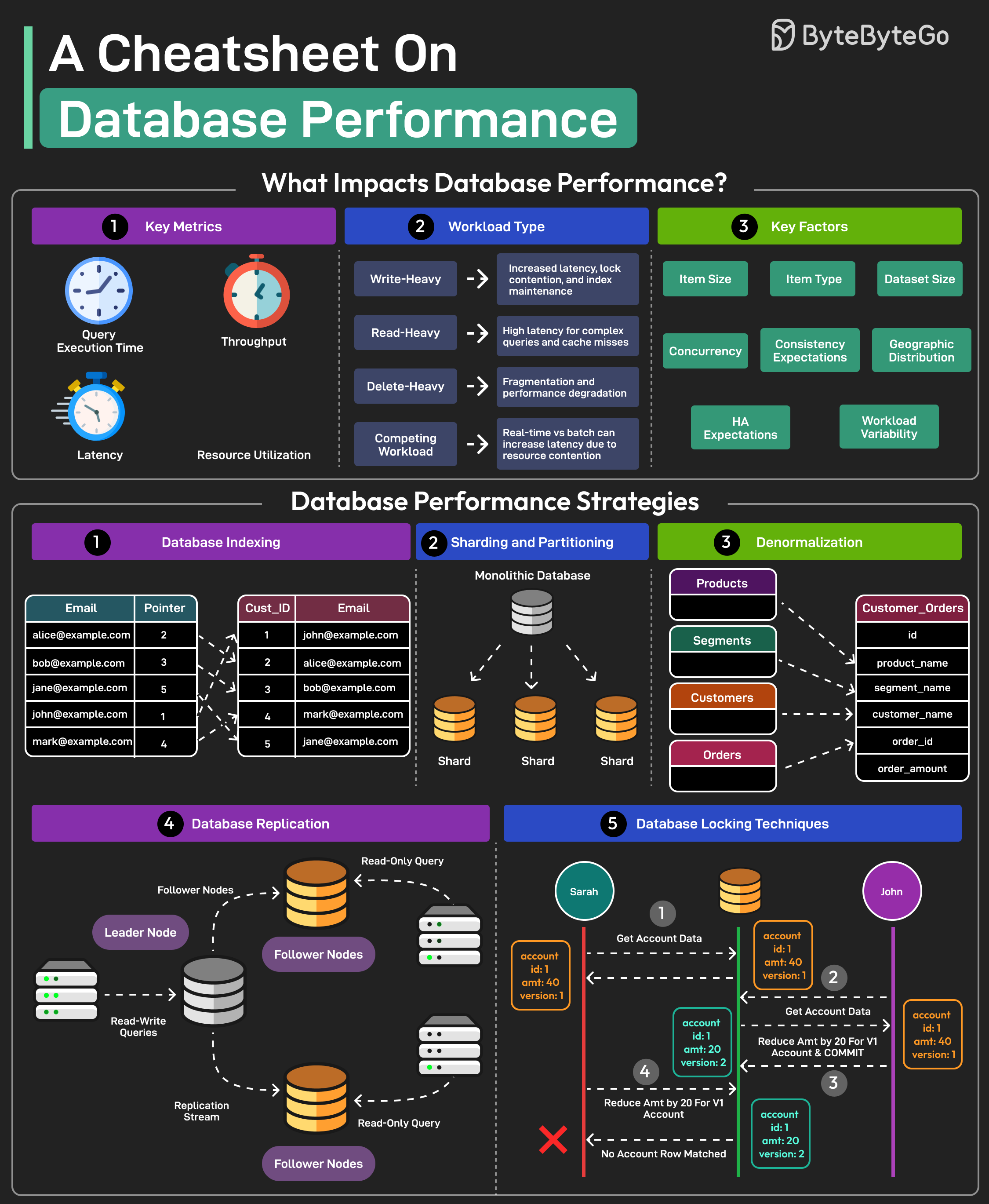
Here’s a cheatsheet on database performance:
1. Indexing
- Purpose: Speed up data retrieval.
- Considerations:
- Over-indexing can slow down writes.
- Regularly review and optimize indexes.
2. Query Optimization
- Techniques:
- Use
EXPLAIN to analyze query plans.
- Avoid
SELECT *.
- Write efficient
WHERE clauses.
3. Connection Pooling
- Benefits:
- Reduces overhead of establishing new connections.
- Improves response times.
4. Caching
- Levels:
- Application-level (e.g., Memcached, Redis).
- Database-level (query cache).
5. Sharding
- Definition: Distribute data across multiple databases.
- Use Cases:
- Handling large datasets.
- Improving write performance.
6. Replication
- Types:
- Master-slave.
- Master-master.
- Purpose:
- Read scaling.
- High availability.
7. Hardware
- Considerations:
- Sufficient RAM.
- Fast storage (SSD).
- Adequate CPU.
8. Monitoring
- Metrics:
- Query response times.
- CPU usage.
- Disk I/O.
9. Normalization/Denormalization
- Normalization: Reduces redundancy.
- Denormalization: Improves read performance (trade-off with redundancy).
10. Partitioning
- Types:
- Purpose:
- Improve query performance.
- Easier data management.
