Best practices for building robust and scalable microservices systems.
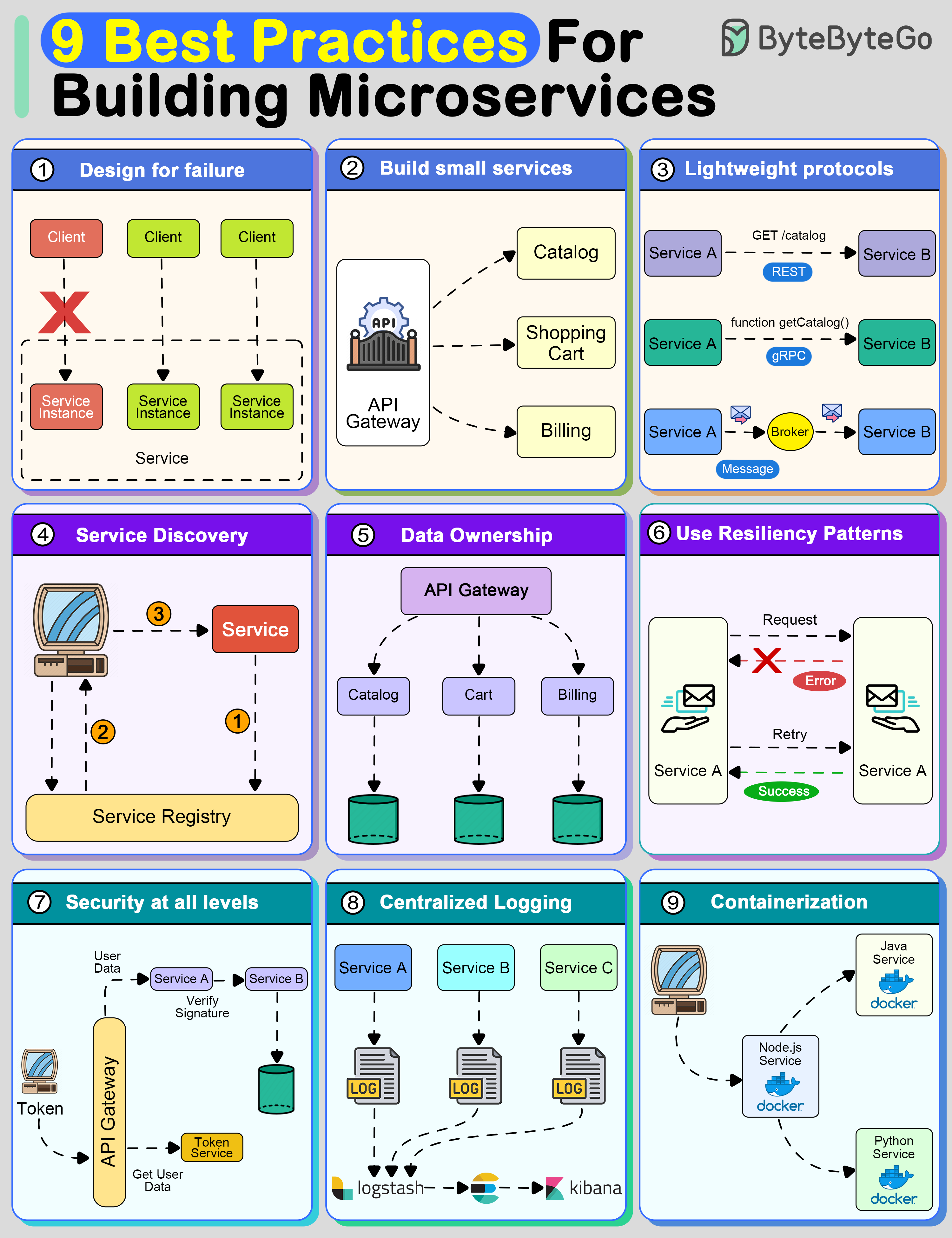
Creating a system using microservices is extremely difficult unless you follow some strong principles.
A distributed system with microservices is going to fail.
You must design the system to tolerate failure at multiple levels such as infrastructure, database, and individual services. Use circuit breakers, bulkheads, or graceful degradation methods to deal with failures.
A microservice should not do multiple things at once.
A good microservice is designed to do one thing well.
Communication is the core of a distributed system.
Microservices must talk to each other using lightweight protocols. Options include REST, gRPC, or message brokers.
To communicate with each other, microservices need to discover each other over the network.
Implement service discovery using tools such as Consul, Eureka, or Kubernetes Services
In microservices, data should be owned and managed by the individual services.
The goal should be to reduce coupling between services so that they can evolve independently.
Implement specific resiliency patterns to improve the availability of the services.
Examples: retry policies, caching, and rate limiting.
In a microservices-based system, the attack surface is quite large. You must implement security at every level of the service communication path.
Logs are important to finding issues in a system. With multiple services, they become critical.
To deploy microservices in an isolated manner, use containerization techniques.
Tools like Docker and Kubernetes can help with this as they are meant to simplify the scaling and deployment of a microservice.